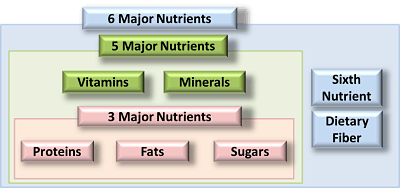
Over the last 20 years in particular there has been an explosion of interest in the area of dietary fiber from the public at large as well as the scientific community to such an extent that dietary fiber is now classed as the sixth major nutrient
There are two main characteristics of fiber that result in almost all of its well documented health benefits and both arise from the simple fact that dietary fiber passes through the small intestine intact and travels to the large intestine where it can be either partially or fully fermented depending on the type of dietary fiber in question.
1) Traditionally, fiber was thought to be good for you because it acted as a way to ‘clean out’ your digestive system by the simple mechanical process of passing through it. There is undoubtedly sound scientific evidence to reinforce this concept. Reduced bowel transit times ensure reduced contact between carcinogenic compounds and mucosal cells and dietary fiber could bind or excrete potential luminal carcinogens like secondary bile acids.11 12
2) More recently however, attention has shifted to the ability of fiber to improve overall gut health which has numerous downstream benefits. This occurs mainly as a result of the change in composition of the gut microbiome. The large intestine contains trillions of bacteria.13
There are ten times more bacteria in our colon than the total number of cells in our bodies. Crucially, ingesting certain dietary fiber components, namely prebiotics, can increase the relative populations of ‘healthy’ bacteria such asBacteroidetes over ‘unhealthy’ bacteria such as Firmicutes.14
These population changes can result in increased levels of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) including butyric acid, propionic acid and acetic acid. Butyrate is the major energy source for colonocytes. Propionate is largely taken up by the liver. Acetate enters the peripheral circulation to be metabolised by peripheral tissues. It is these SCFAs that are now believed to be responsible for many of the health benefits associated with dietary fiber.15
In recent years, food manufacturers have taken advantage of the growing body of scientific knowledge in this area to develop prebiotic and probiotic fibers as foods and food ingredients that can produce beneficial health effects. Regulatory bodies closely monitor health claims and rule on exactly what can and can’t be claimed on a packages label. For more information on the regulatory aspects of dietary fiber please see the section on dietary fiber re gulations .